Bonds are fixed income instruments, which the governments and entities issue to raise money for financing their projects, expenditures and other activities. In this, the investor purchasing bonds in India basically lends money to the bond-issuing entity. In return, the entity pays interest at periodical intervals (typically monthly/quarterly). When the bond reaches its maturity date, the bondholder gets back the principal value (face value) of the bond. Thus, bondholders can be considered as creditors for the bond issuers.
Bonds in India
Bonds in India can be a great option for earning stable returns. Start investing with just Rs. 1,000 and earn monthly/ quarterly interest at Paisabazaar.

Explore Bonds by Category
High Yield

ICRA BBB
You Invest
₹9,952
Returns (YTM)
13.25%
You Get
₹11,493
Today
15 months
Invest in Tencent Backed, Digitally-Driven NBFC Managing an AUM of 1,700+ Cr
You Invest
₹9,952
Returns (YTM)
13.25%
You Get
₹11,493
Today
15 months
Invest in Tencent Backed, Digitally-Driven NBFC Managing an AUM of 1,700+ Cr
ICRA BBB
ACUITE BBB+
You Invest
₹9,803
Returns (YTM)
13.25%
You Get
₹12,680
Today
34 months
Listed NBFC, 670+ Cr AUM with 100% Secured Lending
You Invest
₹9,803
Returns (YTM)
13.25%
You Get
₹12,680
Today
34 months
Listed NBFC, 670+ Cr AUM with 100% Secured Lending
ACUITE BBB+

CARE BBB+
You Invest
₹1,01,307
Returns (YTM)
12.75%
You Get
₹1,17,652
Today
28 months
Listed NBFC backed by Kedaara Capital with 47% Capital Adequacy Ratio
You Invest
₹1,01,307
Returns (YTM)
12.75%
You Get
₹1,17,652
Today
28 months
Listed NBFC backed by Kedaara Capital with 47% Capital Adequacy Ratio
CARE BBB+
What are Bonds?
How to Buy Bonds through Paisabazaar?
Get up to 13.25% from bonds in 5 simple steps
Step 1: Login to your Paisabazaar account
Step 2: Select the Bonds
Step 3: Complete the KYC process
Step 4: Enter bank details
Step 5: Link your demat account
Types of Bonds
Bonds Interest Rates
Bonds interest rate is the interest rate a bond issuer promises to pay on a bond’s face value. More simply, it is the amount bondholders receive periodically on their bond investment. So, let’s say if a bond has a face value of Rs 100 and a interest rate of 8.24%, then the annual coupon (interest earnings) would be Rs. 8.24.
Based on coupon rate, bonds are categorised as fixed rate bond and floating rate bonds. In case of fixed rate bonds, the interest payments remain fixed or unchanged till the bond’s maturity date. However, in case of floating rate bonds, the coupon rate is reset at predefined intervals and is based on a pre-specified market-based interest rate. Thus, interest payments may vary during the bond tenure.
Why Invest in Bonds through Paisabazaar?
High Returns
Earn fixed returns of up to 13.25%.
Low Risk
Invest in a range of highly rated (AAA-BBB) corporate bonds.
Flexible Payout
Get fixed returns credited in your demat linked bank account every month/ quarter.
Low Investment
Start investing with as little as Rs. 1,000.
Safety & Security
Invest in SEBI-regulated senior secured bonds to enjoy higher claim priority over shareholders in case of default or liquidation.
Sell Anytime
Sell bonds anytime through Paisabazaar.
Transparency
Real-time price discovery and assured transaction.
No brokerage/commission
Invest without paying brokerage or commission fee.
End-to-end digital process
Enjoy seamless end-to-end digital process.
Bonds Video Tutorials
People also search for
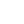
How are Bonds Rated?
6 Benefits of Investing in Bonds in India
Bonds offer several key benefits, including steady income generation, capital preservation, and portfolio diversification, making them a cornerstone of a balanced investment strategy.

Steady Income Stream:
Bonds usually offer fixed interest at regular intervals, providing investors a steady income stream.

Capital Preservation:
The principal of bonds is repaid at maturity, making them ideal for those seeking capital protection amid market volatility.

Diversification:
Investing in bonds can offset the risks associated with more volatile assets like stocks.

Lower Volatility:
Bonds usually show lower price volatility than stocks, offering stability to risk-averse investors.

Predictable Returns:
Bonds offer fixed interest and guarantee to return the principal at maturity, helping investors estimate their future returns and plan their finances in advance.

Potential for Capital Gains:
Investors usually hold bonds for income, however, they can also provide profits if they are sold at higher prices before maturity.
Things to Consider before Investing in Bonds
Here are a few points that investors should consider before investing in bonds in India:
Paisabazaar Bonds in News
How to Buy Bonds through Paisabazaar?
Get up to 13.25% from bonds in 5 simple steps
Step 1: Login to your Paisabazaar account
Step 2: Select the Bonds
Step 3: Complete the KYC process
Step 4: Enter bank details
Step 5: Link your demat account
FAQs
Bonds Articles
View All ArticlesCheck Top Bond Offers with Assured Returns of up to 13.25%
Paisabazaar is a loan aggregator and is authorized to provide services on behalf of its partners
*Applicable for selected customers