Paisabazaar app Today!
Get instant access to loans, credit cards, and financial tools — all in one place
Our Advisors are available 7 days a week, 9:30 am - 6:30 pm to assist you with the best offers or help resolve any queries.
 Get the App
Get the App

Get instant access to loans, credit cards, and financial tools — all in one place

Scan to download on

Get your Free Credit Report with Monthly Updates





Let’s Get Started
The entered number doesn't seem to be correct
Note: The information on this page may not be updated. For latest updates, click here.
The introduction of Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India in July 2017 has led to major reformed of the country’s indirect tax regime. It was introduced with the goal of “One Nation, One Tax” and is still a work in progress. But how did the idea of implementing GST in India come up? When was the GST Bill introduced and passed in the Parliament? And how did the GST Bill finally become the GST Act 2017? Read this article to understand the journey of GST in India starting from the earliest recommendations for a proposed GST Bill to the GST Act of 2017.
Table of Contents :
GST is a comprehensive indirect tax that has replaced a number of indirect taxes, such as VAT, excise duty, entertainment tax and additional duties of customs. It is multi-stage in nature, as it is levied at all stages from manufacturing to final consumption. Moreover, it is applied at every point of sale. SGST and CGST are levied in case of intrastate sale, while IGST is levied in case of interstate sale of goods and services. Another major characteristic of GST is its destination-based application. In other words, GST is levied at the point of consumption and not at the point of production. Now that we have understood what is GST and its major features, let us see how it came into effect in the subsequent section.
Read more about GST.
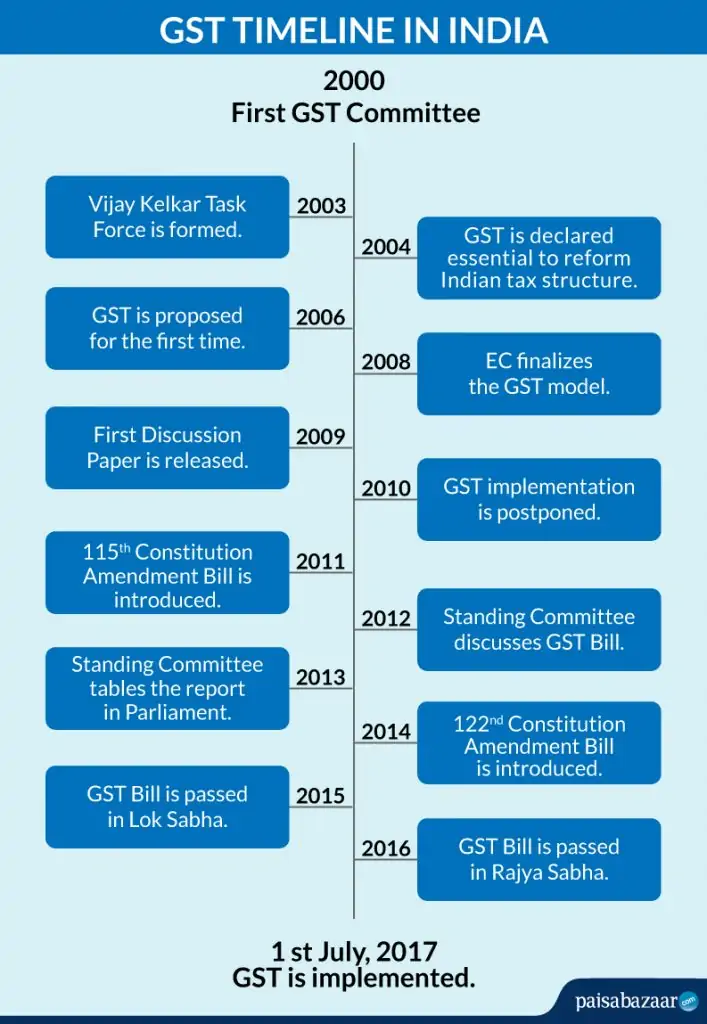
Following is the timeline from conception to implementation of the biggest tax reform, called GST.
GST has revolutionized the indirect tax system of India. It has taken 17 long years of hard work and planning to create the GST model, which has not only simplified the tax system but has also reduced tax burden on common man. Let us understand more about its advantages in this section.
GST has following 3 components:
Additionally, GST Compensation Cess is levied on certain notified goods and services to compensate for potential losses suffered by manufacturing states.
Must Read: Types of GST.
GST has been implemented with the goal of “One Nation, One Tax”, and consequently has subsumed the following indirect taxes levies by Centre and State.

Key taxes subsumed by GST implementation include:
Subsumed taxes earlier levied by the State:
| Particulars | Pre-GST Regime | GST Regime |
| Number of Taxes | Multiple indirect taxes including cess and VAT. | One indirect tax for the entire nation. |
| Cascading effect/ tax on tax | Existed. | Eliminated. |
| Sales Tax on Services | Central Sales Tax (CST) & States Sales Tax (SST) were collected. | Subsumed in GST. |
GST Expert Assistance by PaisabazaarFinding it difficult to avail online services related to GST? Paisabazaar’s offline stores provide expert assistance for GST services. Get step-by-step expert guidance for GST registration, GST filing and GST certificate. Once your GST is set up, you can apply for a business loan to scale your business through Paisabazaar. |
What is the effect of GST on tobacco and tobacco products?
Under the new GST regime, tobacco and tobacco products are taxed at 18% to 28%. Additionally, Central Excise Duty may be levied on these goods.
Also Read: GST Rates- Complete List of Goods and Services Tax Slabs
What is the meaning of Dual GST?
Dual GST refers to the concept of fiscal federalism, where both Centre and State levy GST to maintain their respective revenues. Please note that in India, both Centre and State levy GST at the same rate, and thus the tax burden on the consumers remain unaffected due to the dual nature.
What is Input Tax Credit?
Input Tax Credit refers to the mechanism, that allows you to save GST by only paying the difference between the tax already paid on raw materials and the tax paid on the final product. For example, you are liable to pay Rs. 300 as GST on the final product, but you had already paid Rs. 100 as GST on raw materials. In this case, you can claim Rs. 100 as Input Tax Credit (ITC) and pay only Rs. 200 as GST on the final product.
What is GSTIN?
GSTIN stands for Goods and Services Tax Identification Number. It is a unique 15-digit alphanumeric code allotted to all GST registered entities.
What is GST Compensation Cess?
GST is a destination based tax. This means that if a product is manufactured in state A but consumed in State B, then GST will be collected by state B and not state A. As a result, manufacturing states feared revenue losses, and hence GST Compensation Cess was introduced. It is levied on certain notified goods and services to compensate for the possible losses incurred by manufacturing states.